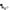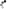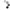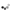|
Consisting of a small vacuum pump, a solenoid valve, a microswitch, cables, pipes and a suction cup, this kit allows to equip the robotic arm "ROBOARM" (not included - see related products) with a system Pick & Place for small objects.
It is mounted instead of the gripper and can rotate at the wrist level thanks to the 1.2 kg•cm RC servo of which the arm is available, allowing, if necessary, the rotation of the piece picked.
The system is based on a suction cup, with a central hole, connected to an aspirator (a small vacuum pump) by means of a three-way electric, which allows switching the suction cup on the pump or on a vent; the latter allows the immediate release of the object taken.
The suction cup is supported by a stem complete with spring that allows you to make soft grips if the arm should press more than necessary on the object to be taken.
The package includes: the pump, the solenoid valve, the microswitch, cables, tubes, suction cup and the plexiglass parts.
Warning: the control electronics and the ROBOARM Robotic Arm are not included. See related products.
|
|
1. the suction cup is positioned on the part to be taken and pushed onto the registered surface until it adheres;
2. The Arduino actuates the vacuum pump through the shield and, as the solenoid valve is a problem connected to the suction cup, the piece is sucked in keeping it attached to it;
3. Arduino is the starting point;
4. at this point Arduino activates the solenoid valve, which switches the common connection on the vent when the depression stops and the object can fall;
5. Once the object has been released, the article returns an arm to its original position and prepares itself for a new withdrawal.
|
 |
|
For the control of the robotic arm with pick and place system, a shield has been used that has been prepared for the control of the servos by Arduino, through the PWM outputs, but also to acquire the analog signal of the potentiometer if we decide to use servomotors with position feedback that "take" the signal of the coaxial potentiometer to the shaft outside.
This function is very useful, for example, for precision positioning, since it allows you to correct any errors or tolerances due to the play of the joints, but also to learn the movements to build sequences to be performed later and automatically; learning can be done by manually bringing the arm in the desired positions, then recording them and then inserting them in a firmware that repeats the relative movements, aiming at reaching the angles of rotation of the servos involved in the movements themselves.
Consider, however, that the system also works smoothly with traditional servos, such as those included in the basic robotic arm described in the last issue.
Among the various functions implemented, the shield provides power to the servos and controls the solenoid of the solenoid valve and the vacuum pump that allow the pick and place.
|
- Arm:
- Arm and forearm length (mm): 160
- Arm height (mm): max. 270
- Height reached by the wrist (mm): max. 310
- Extension (including gripper) (mm): max. 400
- Arm rotation on support base: 180°
- Base (mm): 145x145
- Top grippers with arched jaws
- Operation through 5 RC servos
- Payload on the wrist: 250 g
- Gripper:
- Opening (mm): max. 65
- Lenght (mm): 45
- RC Servo motor 13 kg•cm:
- Operating Speed: 0.17 s / 60° (@ 4,8 V no load)
- Operating Speed: 0.13 s / 60° (@ 6 V no load)
- Torque: 13 kg·cm (@ 6 V)
- Operating voltage: 4,8 to 6 V
- Metal Gears
- Dimensions (mm): 40,7x19,7x42,9
- Weight: 55 grams
- RC Servo motor 1,2 kg•cm:
- Operating Speed: 0.12 s / 60° (@ 4,8 V no load)
- Operating Speed: 0.11 s / 60° (@ 6 V no load)
- Torque: 1,2 kg·cm (@ 4,8 V)
- Operating voltage: 4,8 to 6 V
- Plastic Gears
- Dimensions (mm): 22x12x29
- Weight: 9 grams
|